Choosing the right method of encryption for your database can be a tricky business. Oftentimes, we find ourselves asking the same question, ‘Which database encryption method is suitable for my database?’ To narrow down some of the options, this blog post will discuss three(3) database encryption methods most widely used: Application Programming Interface (API), Plug-In, and Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
Encryption can take place from the database engine all the way to the application layer. Moreover, encryption at different layers would require different modification of the source code. For example, encryption at the application requires extended modifications, while encryption at the database engine would require less.
The API Method
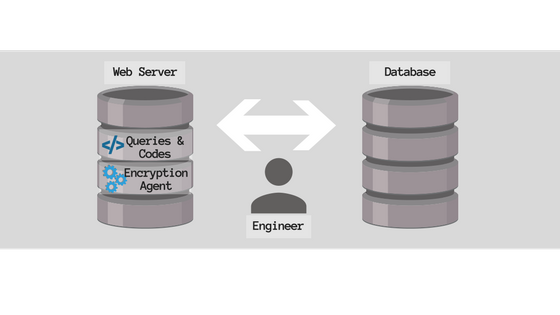
API method encryption occurs in the application layer. This method requires the engineer to use a provided code change function (encryption agent) to edit relevant parts in the web server in order to apply the encryption. API method is applicable regardless of the database product types such as Oracle, ALTIBASE, or MSSQL, and does not impose any additional burden on the DBMS.
However, the API method can be time-consuming when there are large volumes of data. This is due to the fact that the encryption process happens before the data enter the database. As such, all queries referenced in encrypted columns must be directly modified in the application, making it a large hands-on effort for engineers.
The Plug-In Method
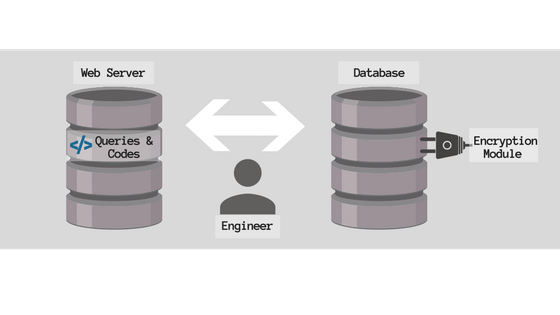
Just like its name suggests, the Plug-In method is basically the concept of attaching an encryption package (encryption module) onto the DBMS. Unlike the API method, this encryption package in DBMS works independently of the application and requires less modification to the query and code. Also, its flexible applicable to both commercial DBMS and open source databases makes it one of the most commonly used encryption method.
The Plug-In method usually allows for index column-level encryption, access control, and auditing. Although almost no action takes place at the web server, engineers will still have to make query changes when encrypting and decrypting large volumes of data for it to run efficiently.
The TDE Method
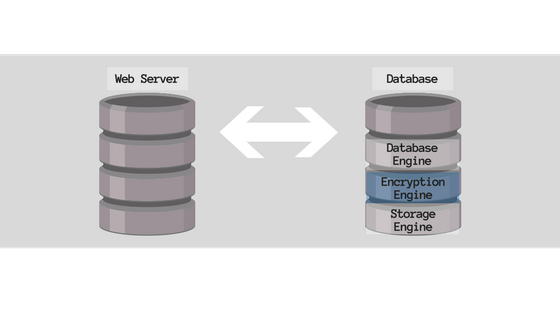
TDE or Transparent Data Encryption — is a database encryption method that requires the installation of an encryption/decryption engine directly into the database engine. This encryption method occurs at the lowest possible system level and requires no modification of the source code of the database environment or application. This means as actions are no longer required on the web server, administrators can easily install and manage the encryption engine in the database.
Furthermore, data are transparently encrypted and decrypted for database users, allowing easier administration for day-to-day encryption operations without the help of engineers.
Among the three discussed database encryption methods, MyDiamo uses the TDE method which enables users to encrypt data easily while maintaining high performance. If you are a security administrator looking for a reliable encryption solution that meets compliance and safeguards sensitive data, MyDiamo might just be the right product for you.